Memory is the most important component of any computer system and its normal operation. The memory is divided into categories by the computer system for various functions, and its types of memory in the computer.
Types Of Memory In Computer:
- Primary Memory or Internal Memory (RAM, ROM, Cache)
- Secondary Memory or External Memory (SSD, CD, Floppy-disk, Magnet-tape)
- Cache Memory (It is part of Primary or Internal memory)
The classification of memory is depicted in the diagram below:
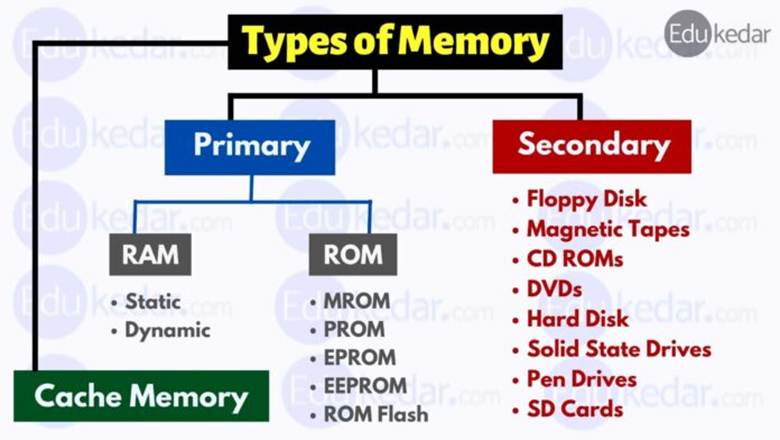
- Primary Memory or Internal Memory (RAM, ROM, Cache)
The major types of primary memory (Internal or Main memory) in a computer is split into following sections:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read Only Memory)
- Cache
★ RAM (Random Access Memory):
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a sort of main memory that can be accessed directly by the CPU and is one of the fastest.
It’s the hardware in a computer device that stores data, programs, and program results temporarily.
It is volatile, which means that if the computer is shut off or if there is a power off, the information contained in RAM will be gone. At any time, all data stored in this types of memory can be read or accessed at random.
Types of RAM Memory in Computer
RAM is divided into two categories:
DRAM (Dynamic RAM):

DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) is a form of RAM that is used to store data dynamically. Each cell in DRAM stores one bit of data.
A capacitor and a transistor are the two components of the cell. Because the capacitor and transistor are so small, they must be stored in millions on a single chip.
As a result, a DRAM chip of the same size can store more data than an SRAM chip of the same size. However, because DRAM is volatile, the capacitor must be recharged on a regular basis in order to retain information.
Characteristics of DRAM
- To keep the data, it must be renewed on a regular basis.
- It’s a little slower than SRAM.
- It can store a lot of information.
- It is made up of a capacitor and a transistor.
- When compared to SRAM, it is less expensive.
- Power usage is reduced.
SRAM (Static RAM):

SRAM (Static Random-Access Memory) is a form of RAM that is used to store static data. It means that data stored in SRAM is active for as long as the computer system is powered up. When there are power outages, however, data in SRAM is lost.
Characteristics of SRAM
- It does not need to be refreshed.
- It faster than DRAM.
- It’s not cheap.
- Power consumption is high.
- Longer life span
- A big size
- It can be used as cache memory.
ROM (Read-Only Memory):
A read-only memory (ROM) is a type of memory or storage medium that is used to store data permanently on a chip. It’s a read-only memory, which means we can only read the information, data, or programs that are stored inside, but we can’t write or modify them.
A ROM is a storage device that holds vital instructions or program data needed to start or boot a computer. It’s a non-volatile memory, which means the data it stores is safe even if the power is turned off or the machine is turned off.
Types of ROM Memory in Computer
Read-Only Memory is divided into five categories:
- MROM
- PROM
- EPROM
- EEPROM
- ROM Flash
1. MROM:
- MROM (Masked Read Only Memory) is a type of memory that is read-only.
- MROM is the oldest type of read-only memory, in which the integrated circuit manufacturer pre-configures the program or data at the time of production.
- As a result, a user cannot alter a program or instruction recorded in the MROM chip.
2. PROM:
- PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of memory that can be programmed.
- It’s a type of digital read-only memory in which the user can only write a single piece of data or program.
- It refers to an empty PROM chip on which the user can only write the desired content or program once with a specific PROM programmer or PROM burner device after that, the data or instruction cannot be modified or erased.
3. EPROM:
EPROM (Erasable and Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of read-only memory that can be erased and reprogrammed.
- EPROM memory is a type of read-only memory in which stored data may only be wiped and reprogrammed once.
- It is a non-volatile memory chip that can store data for a minimum of 10 to 20 years when there is no power source.
- If we want to erase any stored data and re-program it in EPROM, we must first put the data via an ultraviolet light for 40 minutes to delete it; then the data is re-created in EPROM.
4. EEPROM:
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read-Only Memory) is a type of memory that can be erased and reprogrammed.
- The EEROM is an electrically erasable and programmable read-only memory that can be erased and reprogrammed using a high voltage electrical charge.
- It’s also a non-volatile memory, meaning that its contents can’t be erased or lost even if the power is switched off.
- The recorded data in an EEPROM may be erased and reprogrammed up to 10,000 times, and the data is deleted one byte at a time.
5. ROM Flash:
Flash memory is a non-volatile storage memory chip that may be programmed or written in small units known as Blocks or Sectors.
- The contents or data of Flash Memory, which is an EEPROM type of computer memory, cannot be lost when the power supply is switched off.
- It’s also utilized to send data from a computer to a digital device.
Cache Memory in Computer

Cache Memory is a chip-based computer memory that is located between the CPU and the main memory.
- It is quicker, high-performance, and temporarily designed to boost the CPU’s performance.
- It contains all of the data and instructions that computer CPUs frequently use.
- It also speeds up data retrieval from the main memory.
- It is faster than the main memory, and because it is so close to the CPU chip, it is frequently referred to as CPU.
Leave a Reply