- Consists of a circular disk, which is coated with a thin metal or some other material that is highly reflective.
- Laser beam technology is used for recording/reading of data on the disk.
- Also known as laser disk / optical laser disk, due to the use of laser beam technology.
- Proved to be a promising random access medium for high capacity secondary storage because it can store extremely large amounts of data in a limited space.
- Has one long spiral track, which starts at the outer edge and spirals inward to the center.
- Track is divided into equal size sectors.
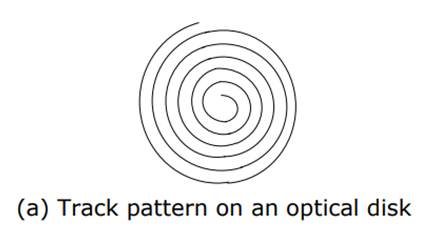
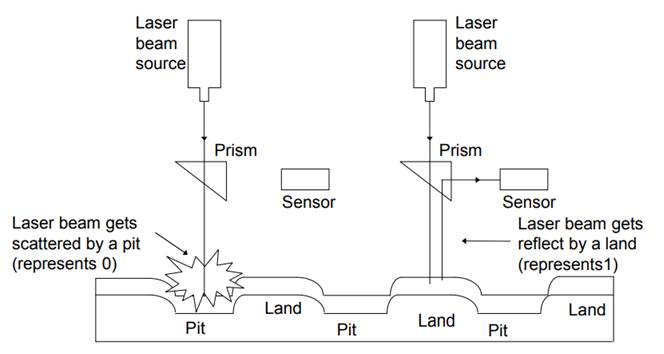
- With optical disks, each sector has the same length regardless of whether it is located near or away from the disk’s center
- Rotation speed of the disk must vary inversely with the radius.
- Leads to slower data access time (larger access time) for optical disks than magnetic disks
- Access times for optical disks are typically in the range of 100 to 300 milliseconds and that of hard disks are in the range of 10 to 30 milliseconds.
- Uses laser beam technology for reading/writing of data
- Has no mechanical read/write access arm.
